Strategic Research RIVM
Annual report 2008
Report 000200904/2009 N.A. Smeenk | J.M.H. Demon
RIVM report 000200904/2009
Strategic Research RIVM
Annual report 2008
N.A. Smeenk J.M.H. Demon
Contact:
Nicoline Smeenk and Annemiek Demon Corporate Affairs
nicoline.smeenk@rivm.nl, annemiek.demon@rivm.nl
© RIVM 2009
Parts of this publication may be reproduced provided the source is properly mentioned:
Rapport in het kort
Strategisch Onderzoek RIVM Jaarrapportage 2008
Dit rapport brengt verslag uit van het Strategisch Onderzoek RIVM (SOR) in 2008, het eigen onderzoeksbudget van het RIVM. Dit onderzoeksgeld is bedoeld om te voorzien in de expertise en kwaliteit om nu en in de toekomst de taken voor de opdrachtgevers adequaat uit te kunnen voeren. In 2008 is ongeveer 12,9 miljoen euro aan SOR besteed.
Het verslagjaar omvat het tweede jaar van de vierjaarlijkse cyclus van SOR-onderzoek die in 2007 is gestart. De uitvoering van de meeste projecten is in 2008 goed op stoom gekomen, wat tot een groot aantal publicaties heeft geleid. Er zijn 78 publicaties verschenen in peer-reviewed tijdschriften en er zijn 62 publicaties ingediend. Bij twee derde van de verschenen publicaties is een medewerker van het RIVM eerste, tweede of laatste auteur. Er zijn ook een groot aantal andere producten opgeleverd, te weten 36 (brief)rapporten, 105 lezingen op internationale congressen, 14 websites, 19 databases en 22 instrumentaria zoals modellen. Daarnaast is de voortgang terug te zien in aanvullende opdrachten en de participatie van het RIVM in internationale projecten. Ook ontwikkelt de samenwerking met externe onderzoeksinstituten zich goed.
Het rapport geeft een indicatie van de wetenschappelijke en maatschappelijke impact van het SOR-onderzoek. Ten opzichte van wetenschappelijke referentietijdschriften is meer dan gemiddeld goed gescoord. De maatschappelijke impact wordt gebaseerd op scores op een aantal indicatoren, die de komende jaren worden gevolgd. De index voor 2008 is voor de meeste speerpunten hoger dan in 2007. Dit is onder meer het gevolg van een groeiend aantal vervolgopdrachten, het gebruik van de resultaten in beleid of richtlijnen en externe verzoeken om advies naar aanleiding van de SOR-projecten. Trefwoorden:
strategisch onderzoek, toekomst, anticiperen, speerpunten, maatschappelijke impact, wetenschappelijke impact
Abstract
Strategic Research RIVM Annual Report 2008
In this document, the National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) reports on progress that was made in 2008 within its Strategic Research Programme (SOR).
The Strategic Research Programme helps the institute to anticipate upcoming research questions, to ensure the quality of its scientific expertise and to participate fully in international research networks. In 2008, about € 12.9 million was allocated to work carried out within the Programme.
The current Programme runs from 2007 to 2010. Most SOR projects reached full speed in 2008, which resulted in a sharp increase in the number of research publications. A total of 78 SOR-related papers were published or accepted for publication in international, peer-reviewed journals, another
62 papers were submitted for publication. Two thirds of the published papers had RIVM staffers as first, second and/or last author.
Strategic research also produced many other products including 36 (letter)reports, 105 talks at international meetings, 14 websites, 19 data bases en 22 tools such as computer models.
Progress could also be measured in terms of RIVM gaining follow-up assignments, taking part in international research projects and further expanding its long-term collaboration networks with other institutes.
This annual report monitors the Programme’s impact on science and society in 2008. Research output quantity rose, while on the whole peer-reviewed research papers were accepted or published in journals with higher-than-average impacts.
To measure the Programme’s impact on society, a number of indicators have recently been developed. Performance on these indicators will be monitored over the coming years. In 2008 the index increased, mainly the result of increasing follow-up assignments, the use of the results in policy and external requests for advice.
Key words:
Contents
Contents 7
1 Introduction 9
1.1 Introduction 9
1.2 Purpose of this report 9
1.3 Reading guide 9
2 2007-2010 research themes 11
2.1 The significance of strategic research for RIVM 11
2.2 Research theme choice and evaluation 11
2.3 Risk Perception, Consumer behaviour and understanding (RPC) 12
2.4 Emergency Response Functions (ERF) 12
2.5 INFectious diseases (INF) 12
2.6 Chronic diseases Intervention and Lifestyle (CIL) 13
2.7 Medicines and Functional Foods (MFF) 13
2.8 Environmental Quality and Health (EQH) 13
3 Strategic research progress in 2008 15
3.1 Monitoring progress 15
3.2 Strategic Research Programme (overall) 15
3.3 Risk Perception, Consumer behaviour and understanding (RPC) 15
3.4 Emergency Response Functions (ERF) 15
3.5 INFectious diseases (INF) 16
3.6 Chronic diseases Intervention and Lifestyle (CIL) 16
3.7 Medicines and Functional Foods (MFF) 17
3.8 Environmental Quality and Health (EQH) 17
4 2008 in numbers 19
4.1 Research quantity indicators 19
4.2 Research quality indicators 19
4.3 Other research output 20
4.4 The impact of strategic research on society 21
4.5 Societal impact summary scores 23
4.6 Finances 23
5 Conclusion and outlook for 2009 25
5.1 General assessment 2007-2010 Programme 25
5.2 Progress in 2008 25
5.3 Midterm review 25
Annex 1 Research programmes and projects 27
Annex 2 Papers from SOR projects in 31
Annex 3 Research quality methodology 42
Annex 4 Reference journals 2008 43
Annex 5 New assignments 51
Annex 6 Indicators for the impact of health research on society 52
1
Introduction
1.1
Introduction
The National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) in the Netherlands has a dedicated budget for initiating and carrying out strategic research. Through its Strategic Research Programme (Strategisch Onderzoek RIVM, SOR), the institute is able to anticipate upcoming research questions, to ensure the quality of its scientific expertise and to participate fully in long-term
international research networks.
The Strategic Research Programme is set up using four-year programme and budget cycles. The current cycle started in 2007. The programme comprises of 6 strategic research themes, which together cover 60 individual research projects.
1.2
Purpose of this report
RIVM reports annually on the progress achieved within its Strategic Research Programme. This report covers activities in 2008 and provides various measures:
• research progress within all 6 research themes; • research output (e.g. papers, talks, other products); • scientific impact of the research;
• its impact on society; • finances.
This report provides measures at the research theme level. A separate Appendix to the report provides further information at individual project level (Strategic Research RIVM , Project progress, appendix to annual report 2008, RIVM report 000200905).
1.3
Reading guide
Chapter 2 restates why the Strategic Research Programme is of vital importance for RIVM and summarizes the scope of its current research themes.
Chapter 3 describes the progress that was made in 2008 in general terms, both at the programme and research theme levels.
Chapter 4 presents and analyses qualitative measures of research output. Chapter 5 sums up with general conclusions.
2
2007-2010 research themes
2.1
The significance of strategic research for RIVM
The National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) is the Netherlands’ most important public research institute in the areas of public health, environment, safety and nutrition. Its primary task is to support the Dutch government in making science-based policy by providing sound and independent counsel. RIVM’s advice typically reflects a large body of scientific evidence and often builds on full risk assessments or risk management procedures.
In addition to this, RIVM carries various executive responsibilities in the areas of national health and the environment. RIVM’s other (international) clients include public organisations such as the World Health Organisation (WHO), the European Commission (EC) and various agencies of the European Union (EU).
Strategic research, as carried out within the Strategic Research Programme (SOR), serves to reinforce the institute’s national and international position and to increase its scientific authority by contributing more to peer-reviewed scientific publications. For RIVM, doing scientific research means connecting with academic research and research communities.
Through its strategic research, the institute aims to anticipate research and policy questions that may arise in the (near) future. Such research, by definition, involves innovations and carries some risks.
Due to the financial structure of an agency, regular commissions prevail. Apart from the new knowledge that is acquired during this work, separate investments are needed to safeguard the institute’s expertise and craftmanship. In one sentence: SOR serves to keep RIVM scientifically well prepared for the day after tomorrow and realize its future professional skills.
The RIVM’s Director-General holds the SOR budget and formally commissions all strategic research. The 2007-2010 Programme comprises about 60 research projects grouped into six strategic research themes. In each of the themes, all projects wil be reviewed midterm and recommendations to RIVM’s management board will be made. Recommendations and management decisions may include continuation with or without adaptations and project discontinuation.
2.2
Research theme choice and evaluation
RIVM’s strategic research must fit within a limited number of carefully chosen research themes. They serve as the Strategic Research Programme’s overall framework. Research themes must align with RIVM’s strategic areas and should anticipate future developments. They are chosen in close
consultation with the RIVM’s Supervisory Board. The six themes of the 2007-2010 Strategic Research Programme were chosen in 2006.
The 2008 review evaluated how research themes have been implemented in research projects. Most themes have grouped various projects into distinct research programmes. All research themes and programmes are summarised below. Annex 1 provides a full list of priorities, programmes and projects.
Much of RIVM’s research is multidisciplinary so overlaps between themes and programmes do occur. Theme coordinators meet frequently to ensure that all research keeps the right focus.
2.3
Risk Perception, Consumer behaviour and understanding (RPC)
Theme purpose
Studies into risk assessment, risk perception and consumer behaviour are highly relevant to many issues in society today. Research within this theme affects one of RIVM’s core competences and is therefore important to most if not all of the institute’s divisions. The theme offers many opportunities for interdivisional cooperation.
Programmes
Research projects in this theme are grouped into two research programmes. One focuses on animal experimentation, both to properly estimate risks and to reduce our dependence on laboratory animals. The other focuses on risk information and quality.
2.4
Emergency Response Functions (ERF)
Theme purpose
In today’s world, governments need to prepare for emergencies. Whether they involve chemical, biological or radiation exposures or other types of calamities, all such emergencies require sensible preparation for an adequate response. In recent years, bioterrorism and infectious disease outbreaks have attracted attention. Other needs include modelling of environmental risks from chemicals or radiation, and research into toxicological effects in humans as well. At least two RIVM divisions need to be fully up to date on safety and emergency response functions.
Programmes
Research projects in this theme are grouped into three programmes: (1) risk assessment methods in emergencies, (2) clinical toxicology and (3) measurement and modelling.
2.5
INFectious diseases (INF)
Theme purpose
The theme includes research into questions ranging all the way from infectious agents to effective epidemiological interventions. Food safety issues are relevant as well. Research within this theme will help reinforce RIVM’s expertise in areas such as immunology, vaccination and genetics. Effect studies and modelling are highly important as well.
Programmes
Research projects in this theme are grouped into three programmes: (1) genomics, (2) immunology and (3) modelling.
2.6
Chronic diseases Intervention and Lifestyle (CIL)
Theme purpose
Chronic diseases and lifestyle changes constitute growing problems and require policy-making at local, national and international levels. Some knowledge about preventive interventions could be
implemented more fully, and new types of prevention should be developed. High-risk groups need to be identified early on and receive special attention. Increasingly, links between life styles and health are being debated, and citizens are encouraged to adjust their behaviours. Food quality, obesity, diabetes, cancer, medical screening, and quality of life are just a few of the issues that are more and more coming together, and the trend will most likely continue. Growing expertise on these interfaces at RIVM will be needed.
Programmes
Research projects in this theme are grouped into four programmes: (1) modelling chronic diseases, (2) healthy aging, (3) quality of care, and (4) economic evaluations.
2.7
Medicines and Functional Foods (MFF)
Theme purpose
More and more, medicines and novel foods become intertwined, and RIVM needs to acquire more expertise in this area. Straightforward risk assessments are moving towards risk-versus-benefit and chain approaches. Also, it is becoming more important to understand system functions in care, and consumer behaviour and understanding need to receive proper attention.
Programmes
Projects within this theme are all highly related so no separate programmes are identified.
2.8
Environmental Quality and Health (EQH)
Theme purpose
Monitoring remains vital in many environmental areas, such as particulate matter. Risk assessments for encouraging healthy environmental conditions or evaluating economical activity are becoming
increasingly important. More research needs to go into identifying behavioural scenarios and risk perceptions. Complicated risk assessments and environmental health impact assessments need to be developed. The EQH theme reflects the diversity of RIVM’s Environment and Safety Division, but other divisions are involved in assessing environmental health effects.
Programmes
Research projects in this theme are grouped into three programmes: (1) risk assessment, (2) environmental health impact assessment and measurement and (3) modelling.
3
Strategic research progress in 2008
3.1
Monitoring progress
Since 2007, progress of strategic research projects is monitored and reported to RIVM’s Director-General on an annual basis. By completing yearly progress reports, project leaders provide information about the project’s goals, progress, products and finances. They report changes in the objectives or approaches and make projections on work and products in the next year. The questionnaires are used by theme coordinators to produce reports at the theme level.
This chapter summarizes 2008 progress in general terms. Research output in terms of papers and reports that were published is given in the next chapter (chapter 4).
Progress reports at the project level can be found in a separate Annex to this report (Strategic Research RIVM, Project progress, appendix to annual report 2008, RIVM report 000200905)
3.2
Strategic Research Programme (overall)
Before 2008, 59 SOR-related research projects had already started. In 2008, another 7 projects got off the ground. Most projects picked up speed during the second year of the programme cycle. Some project leaders, however, noted that government cutbacks had made it more difficult to provide sufficient human resources to the projects. Solutions included outsourcing of some of the work and strengthening partnerships.
3.3
Risk Perception, Consumer behaviour and understanding (RPC)
All RPC projects began in 2007 and are now very close to delivering products. For example, the Proteomics for population screenings project reported important progress in particular on new diagnostic methods. The Toxicogenomics in Risk Assessment project reports that genomics-related techniques appear to go well with innovative risk approaches. The techniques also hold promise for other RIVM divisions and the Netherlands Toxicogenomics Centre in which RIVM participates. Follow-up research to support innovative risk assessment procedures seems promising. The Nano-Technology, Potential Risks project has earned additional outside funding. The Effective Use of Performance Indicators project and the Methods for Dietary Exposure Assessment project both were productive as well. Given the progress, there are no reasons to make adjustments within the RPC theme.
3.4
Emergency Response Functions (ERF)
The ERF theme mostly consists of new projects, which in 2008 picked up speed, as can be gleaned from the data on output presented in the next chapter. Various projects attracted additional assignments. Researchers joined international research efforts and initiated other collaboration arrangements with outside partners. Some project leaders noted that a combination of staff departures and government cutbacks had made it more difficult for them to provide human resources. As a result, some of the work
was outsourced or handled jointly with outside partners. A SOR-related strategic alliance with Utrecht University was highlighted by the inaugural lecture of a RIVM-based part-time professor. In one project, 2008 scientific output levels have triggered specific attention.
3.5
INFectious diseases (INF)
Progress in most INF projects was according to expectations, although some projects reported delays in publishing results. The theme comprises of three programmes: genomics, immunology and modelling. Genomics projects included (1) whole-genome analysis of M. tuberculosis, (2) microarrays to map pertussis adaptation, (3) whole-genome analysis of B. pertussis and (4) a study on Rickettsia in ticks (started in 2008). Progress in genomics projects was good, including efforts to analyse and present genomics data. Private parties are showing interest
The immunology programme is considered important because immunology is not part of the Centre for Infectious Disease Control Netherlands (CIb’s) usual work for the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. The programme involves four projects: (1) immunomodulation by helminth infections, (2) memory immunity, (3) immune pathways in vaccination and (4) host response to Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). Progress in the immunology projects was less than originally planned mainly due to difficulties in getting results published. Several papers are projected to be published in 2009, however. Modelling projects focused on (1) the future of MRSA in the Netherlands, (2) tracking emerging epidemics, (4) epidemic modelling of molecular data and (4) chlamydia positivity (started in 2008). The mathematical modelling projects yielded interesting results, leading to published research papers. Also, a lecture at a meeting on SOR at the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport in October 2008, demonstrated the programme’s appeal to policymakers.
Within the INF theme, an open call for proposals was held. After peer review four new projects were selected (marked in Annex 1), two of which (both related to food born norovirus infections) fell outside the scope of the three programme’s.
Three projects receive co-financing from the European Commission: VITAL, immune pathways in vaccination and chlamydia positivity. Duration of projects varies from two to four years. Almost all projects have strategic alliances with universities. In five projects, a PhD student carries out part of the research.
3.6
Chronic diseases Intervention and Lifestyle (CIL)
Most projects within the CIL theme made good progress in 2008. Two new projects were launched: (1) chronic disease in children and (2) communicating about uncertainty in economic evaluations. Some projects attracted international attention, such as the one on knowledge transfer. By late 2008, two projects were completed successfully. The first, on calculations of future healthcare costs, produced three published papers. The second, a preliminary study on primary health care, led to a plan for a third national study on the same subject, which is now being considered by the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (VWS).
3.7
Medicines and Functional Foods (MFF)
All projects from the 2003-2006 SOR cycle were fully completed in 2008. A new project, called Biothree, was launched. In the Chronic drug use and autoimmunity project, an interesting association between chronic use of statins and an above-average prevalence of arthritis was found. The MAGIC project, on drug use in children, is beginning to bear fruit as well. After a difficult first year, research within the MFF theme has clearly begun to make progress.
3.8
Environmental Quality and Health (EQH)
Most projects within the EQH theme made good progress. Solutions were found to start-up problems in the previous year, such as difficulties in attracting qualified staff. They include arrangements with other research organisations such as PhD student contracts. Research output has picked up speed. Some projects report additional assignments and participation in international projects.
Among the year’s highlights was the Flash Environmental Assessment Tool (FEAT), a spin-off from the EIA (Environmental Impact Assessment) project. Within a short time frame, at the request of the United Nations, RIVM researchers developed a tool to quickly identify acute environmental risks immediately following disasters in developing countries. SOR-based methodology was also used in studies on disease prevalence among people living close to a CORUS location in the Netherlands. One of the studies, on cancer prevalence, was completed in 2008 and received good marks during an international audit. Some project leaders in the EQH theme noted that government cutbacks had made it more difficult to provide sufficient human resources. Because of that, some of the work was outsourced or handled jointly with outside partners.
SOR-related strategic alliances with Utrecht University and Radboud University (Nijmegen) were highlighted by inaugural lectures of RIVM-based part-time professors.
4
2008 in numbers
4.1
Research quantity indicators
Research output in terms of scientific papers or reports that were published is presented below. Annex 2 contains references to published and accepted papers for each research project.
The 2007-2010 Strategic Research Programme
In 2008, a total of 78 SOR-related scientific papers were published or accepted for publication in international peer-reviewed journals. This is roughly 15 % of the total number of RIVM publications. Two thirds (52) of these papers had RIVM staffers as their first, second and/or last author, signifying particular importance of the research for the institute. Another 62 papers were submitted for publication to editors of similar journals. One PhD thesis was completed in 2008. Of course, work for this thesis had been carried out in large part in previous years.
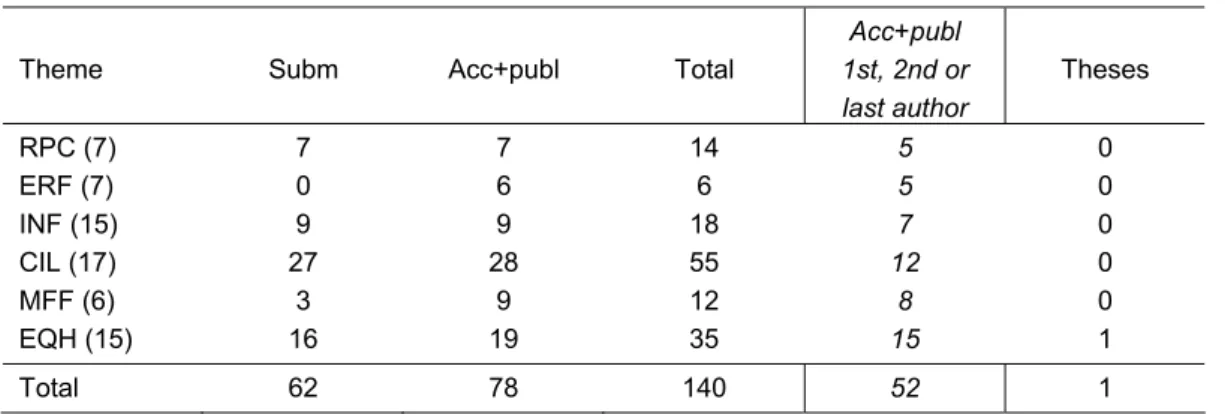
Table 4.1 presents a breakdown of these numbers per theme. Table 4.1 Number of research papers SOR 2007-2010
Theme Subm Acc+publ Total
Acc+publ 1st, 2nd or last author Theses RPC (7) 7 7 14 5 0 ERF (7) 0 6 6 5 0 INF (15) 9 9 18 7 0 CIL (17) 27 28 55 12 0 MFF (6) 3 9 12 8 0 EQH (15) 16 19 35 15 1 Total 62 78 140 52 1
Between brackets the number of projects per theme Subm submitted for publication
Acc accepted for publication Publ published
Compared to 2007, the number of scientific papers accepted and published almost doubled, demonstrating that most projects reached full speed.
One project from the 2003–2007 Strategic Research Programme cycle was ongoing in 2008 and produced one scientific publication that same year.
4.2
Research quality indicators
In 2002, consultations with RIVM’s Scientific Advisory Board led to the selection of quality indicators for strategic research. The indicators were based on methodology developed at the Faculty of
Veterinary Medicine of Utrecht University. They were used for the 2003-2006 Strategic Research Programme and, with minor modifications, are used for the current cycle as well.
The methodology is based on the impact factors of all journals in which papers were published. It measures the quality, not the quantity of the output. For every research theme, the average impact factor is calculated from journals that accepted and published its papers. Scores are compared to a ‘standard’, which is the average impact factor of all reference journals relevant for that particular theme (not including journals with impact factors >15). The comparison leads to assessments on a five-point scale where 5 is highest, 1 is lowest and 3 represents an average, perfectly acceptable score. A more detailed explanation of the methodology is given in Annex 3. A list of reference journals per theme is given in Annex 4.
Table 4.2 presents average impact factors and assessment scores for all research themes. Table 4.2 Indicators of scientific quality per theme 2007-2010: average impact factors
RPC ERF INF CIL MFF EQH
Average impact factor 2007 4.787 - 3.937 4.508 - 2.626
Standard 2007 3.650 2.598 3.878 3.321 3.160 2.043
Assessment Class (1-5) 5 - 3 5 - 4
Average impact factor 2008 3.786 2.543 5.501 8.807 2.913 3.305
Standard 2008 3.569 2.764 3.932 3.466 3.163 2.217
Assessment Class (1-5) 3 3 5 5 3 5
A number of observations have been made on the use of this methodology:
• Assessment scores should be seen as indicative only. Impact factors vary greatly, and researchers are able to influence the standard against which they are measured by providing lists of reference journals.
• Assessment scores do not take into account the quantity of the output, just the quality of the journals in which output was published. One paper in a top journal may seem to outperform twenty papers in less outstanding but still highly respectable journals. Therefore, Table 4.2 should always be evaluated together with the number of papers published (Table 4.1).
• RIVM’s primary purpose is helping answer policy questions. While achieving high research quality is highly valued within the institute and elsewhere, it will not always be possible. That may be true in particular for research that is aimed at developing new methods.
Such observations notwithstanding, overall results were very good. Most themes achieved higher impact scores than the pre-achieved standard. Themes INF, CIL and EQH were assessed as Class 5, while none of the other themes was assessed lower than Class 3.
4.3
Other research output
The 2007-2010 Strategic Research Programme
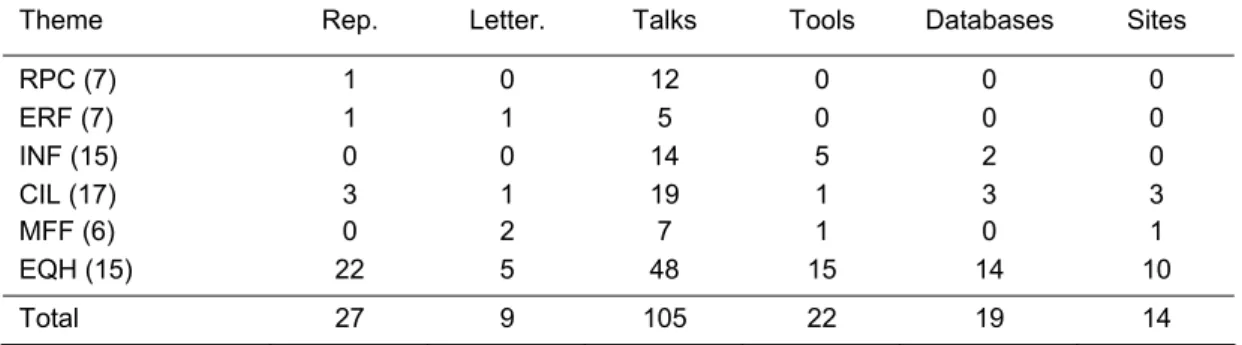
Strategic research also produced many other tangible products. 36 (letter) reports were written, 105 talks at international meetings presented, 14 websites built, 19 data bases set up en 22 tools (such as computer models) created. Table 4.3 presents a breakdown of these numbers per theme.
Table 4.3 Other research products
Theme Rep. Letter. Talks Tools Databases Sites
RPC (7) 1 0 12 0 0 0 ERF (7) 1 1 5 0 0 0 INF (15) 0 0 14 5 2 0 CIL (17) 3 1 19 1 3 3 MFF (6) 0 2 7 1 0 1 EQH (15) 22 5 48 15 14 10 Total 27 9 105 22 19 14
Between brackets the number of projects per theme Rep. Reports
Letter. Letter reports
Talks Talks presented at international meetings Tools Tools (e.g. models)
Databases Databases Sites Web sites
4.4
The impact of strategic research on society
According to the Scientific Advisory Board, applied research carried out at the institute should not only have strong scientific merit but should bring value for society as well. In order to properly assess that value, the Board has asked the institute to develop straightforward and cost-effective indicators by which to measure the Strategic Research Program’s impact on society, and to begin monitoring that impact as part of the 2007-2010 program cycle.
As of yet, no general consensus exists on the best methodology by which to assess the impact of research on society. What's more, there is not even a generally accepted definition of what the impact of research on society is. For RIVM, a definition proposed by Eijsackers (WUR, 2007) seems the most applicable: Research has an impact on society when its outcomes can be used by governments,
industry, non-governmental organizations or the general public because they: • could lead to direct applications;
• offer solutions to social problems or address social developments; • answer questions that arise in society or fulfil societal needs.
Also, research should address a significant problem or issue, i.e. serve a general interest.
RGO guidelines on health research impact indicators
In December 2007, the Advisory Council on Health Research (RGO), a body advising the Dutch government on health and health services research, published a report on assessing the impact of research on society. Titled ‘Research that matters’ (“Onderzoek dat ertoe doet”), the report offered a list of indicators that gauge the impact of health research. The Council stressed the limited experience with applying such indicators and warned against putting too much emphasis on numerical values as of yet. The Council rather presented its list as a rough guide that should be experimented with. In setting up such experiments, users should select their own indicators based on the general list.
From RGO’s general list (see Annex 6), RIVM has selected a short list of indicators that seem most suitable to measure the impact of the institute’s Strategic Research Program. In making the selection, RIVM included the following rationale:
• RIVM’s strategic research has a particular focus – it is primarily targeted at demand that will most probably materialize in the future.
• Many factors contribute to measurable health impacts, and typically it will be hard to contribute such impacts directly to the strategic research program itself.
Strategic Research RIVM impact indicators
Obviously all RIVM research, including that carried out as part of the Strategic Research Program, should ultimately have positive effects on society. Such effects, however, will usually become visible only at a much later time. All selected indicators may be called indirect: we may assume that, when third parties apply RIVM research outcomes, or when RIVM is asked for advice based on the fruits of its work, there will most probably be future impact. Following the same line of thinking, follow-up assignments were added as indicators because they can be seen as clear signs of outside interest in RIVM research results.
Some indicators on the list of the Advisory Council on Health Research could indeed be very meaningful when applied to RIVM as a whole. These include, for example, contributions to
professional education, informing the public through authorized web sites, and references to research in public media. However, it would be very difficult to directly contribute performance on such indicators to strategic, long-term research. Therefore these indicators were not deemed suitable for measuring societal impact of the Strategic Research Program. The Advisory Council on Health Research also presented a list of indicators for the assessment of economic impact of health research. For similar reasons, these indicators were also deemed not very suitable for measuring the impact of RIVM’s strategic research.
In the end, the following process- and product-based indicators were identified. For all these indicators, performance will be assessed and quantified annually:
• follow-up assignments from primary clients; • follow-up assignments from secondary clients;
• use of outcomes in guidelines, regulation, policies and so on; • requests for advice from third parties;
• participation in international bodies.
Strategic Research Programme 2007-2010
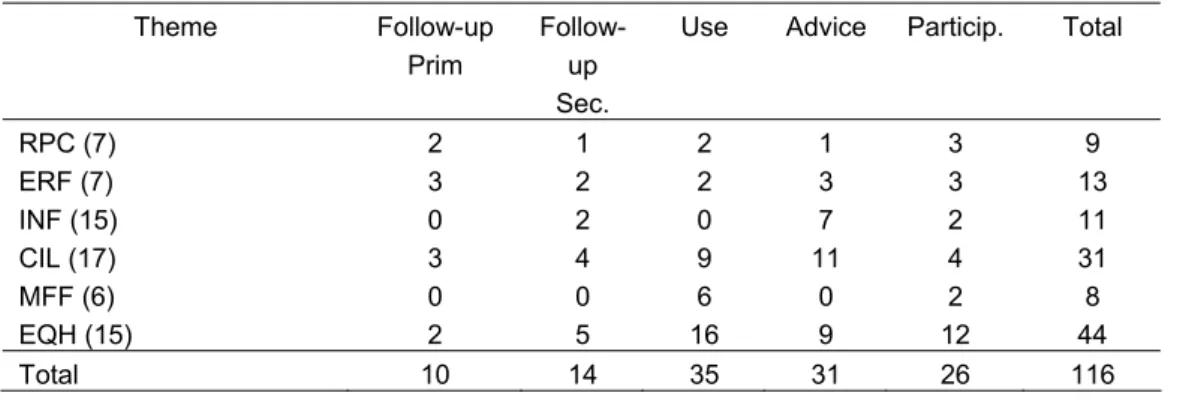
Table 4.4 presents performance scores on selected societal impact indicators for all research themes. Table 4.4 Research themes and their performance on selected societal impact indicators
Theme Follow-up Prim
Follow-up Sec.
Use Advice Particip. Total
RPC (7) 2 1 2 1 3 9 ERF (7) 3 2 2 3 3 13 INF (15) 0 2 0 7 2 11 CIL (17) 3 4 9 11 4 31 MFF (6) 0 0 6 0 2 8 EQH (15) 2 5 16 9 12 44 Total 10 14 35 31 26 116
Follow-up Prim. Follow-up assignments from primary clients Follow-up Sec. Follow-up assignments from secondary clients
Use Use of outcomes in guidelines, regulation, policies and so on. Advice Requests for advice from third parties
Particip. Participation in international bodies
4.5
Societal impact summary scores
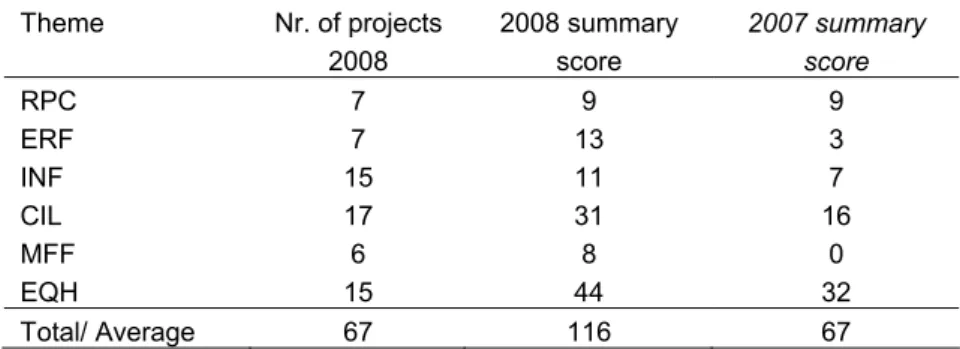
Within the Strategic Research Program, the various research themes differ significantly in terms of budgets and numbers of projects. As of yet, there is no absolute standard to which a theme’s performance can be compared. For now, the scores can only be used to compare individual research themes and to monitor the Strategic Research Program’s impact over the years. Some in the field have experimented with methodologies that use weighted performances. Weightings could be based on differences between areas of research, for example. At this point, no weightings have been applied to calculate scores for RIVM’s Strategic Research Programme. This might change in the future, for example based on discussions within RIVM’s Board of Supervisors. Table 4.5 presents societal impact summary scores for each of the research themes in 2008.
Table 4.5 Research themes and their societal impact summary scores
Theme Nr. of projects 2008 2008 summary score 2007 summary score RPC 7 9 9 ERF 7 13 3 INF 15 11 7 CIL 17 31 16 MFF 6 8 0 EQH 15 44 32 Total/ Average 67 116 67
Annual reports will continue to present societal impact summary scores in the future, making it easier to assess impact trends over time. For example, Table 4.5 shows that between 2007 and 2008 societal impact summary score for RPC was stable, while scores rose markedly for the other themes.
RIVM monitors the development of methodologies to assess societal impact used by others in the health research field. If possible and needed, newly developed methodologies will be incorporated into future Strategic Research Programme reports.
4.6
Finances
1Prior to 2007, the strategic research budget frequently ended up being not fully exhausted. Therefore, research in the 2007-2010 Programme cycle was budgeted at 120 percent of the available funds. In 2008, €12.8 million was allocated while €11.0 million was actually available. In the end, more than
100 percent of the available funds were spent. The surplus has been accounted for through adjustments in the policy budget of the Director-General (DG).
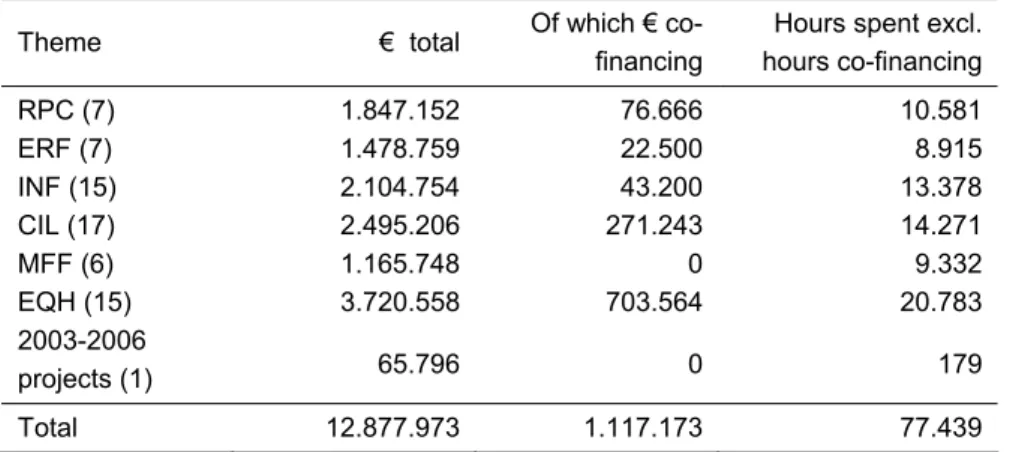
Table 4.6 presents the funds that were spent for each theme out of the DG’s 2008 budget.
The table does not include expenditures that were paid using funds from external sources, such as funders who co-finance research by matching RIVM’s own funds. In the table, the second column presents the amounts invested by RIVM in co-financed projects. The table’s third column presents the number of hours that were put in by RIVM staff, not including hours paid from RIVM funds invested in co-financed projects. (Accounting rules stipulate that such hours should be reported elsewhere.). Table 4.6 Budget spent per theme
Theme € total Of which €
co-financing
Hours spent excl. hours co-financing RPC (7) 1.847.152 76.666 10.581 ERF (7) 1.478.759 22.500 8.915 INF (15) 2.104.754 43.200 13.378 CIL (17) 2.495.206 271.243 14.271 MFF (6) 1.165.748 0 9.332 EQH (15) 3.720.558 703.564 20.783 2003-2006 projects (1) 65.796 0 179 Total 12.877.973 1.117.173 77.439
5
Conclusion and outlook for 2009
5.1
General assessment 2007-2010 Programme
Assessments of progress within the Programme’s research have not yielded indications that research themes and/or projects should be adjusted in 2009. By late 2008, all but one of the projects from the 2003-2006 Programme cycle had been completed.
5.2
Progress in 2008
Generally speaking, research output from RIVM’s Strategic Research Programme increased markedly between 2007 and 2008. (An increase was to be expected, however, since most research projects were launched in 2007.) On the whole, papers were accepted or published in journals with higher-than-average impact. Average societal impact index scores rose since 2007. In conclusion, 2008 was a good year for RIVM’s strategic research.
5.3
Midterm review
All projects that were halfway by late 2008, i.e. four-year projects that started in 2007, will undergo a midterm review in 2009. The midterm review serves to test the quality and the progress of individual projects. Evaluations will be carried out by theme coordinators based on a list of questions drawn up by RIVM’s Director-General. They take into account original plans as well as 2007 and 2008 progress reports, and they consult with independent experts inside and outside the institute. Based on the midterm review, theme coordinators will present recommendations for each project to the Director-General. The 2009 annual report will report on the recommendations and the decisions that will be based on them.
5.4
Preview: New projects in 2009
In the first six months of 2009, four additional research projects were launched as part of the 2007-2010 Strategic Research Programme. Two of these fall within the INF theme, one in the RPC theme and one in the MFF theme. Annex 7 lists full titles and project leaders. Outside review was applied to assess these projects’ proposals.
Annex 1 Research programmes and projects
S = Projects started in 2008 C = Projects completed in 2008
Theme: RPC
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Experimental (animal) studies in risk assessment
CIb 230126 Ing. J.H.J. Reimerink
Proteomics for population screening
VGC 340010 Mw. Dr. M. Luijten Toxicogenomics in risk assessment
VGC 350010 Dr. Ir. M. C. Ocké Methods for dietary exposure assessment VGC 340050 Dr. L.T.M. van de
Ven
Alternatives for animal testing
VGC 340030 Dr. W. H de Jong Nanotechnology, potential risks Information to consumers VenZ 270136 Drs. H.C. Ossenbaard Getting.Better.nl VenZ 260196 Dr. W.C. Graafmans
Effective use performance indicators
Theme: ERF
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Measuring and modelling
CIb 330006 Dr. B.J. van Rotterdam
Biothreat DNA micro-arrays
MEV 620001 Dr. P.A.M. Uijt de Haag
QRA
MEV 630007 Dr. Ir. L. Grievink Rapid assessments after disasters C MEV 609001 Mw Dr. S.M. Hoffer T-attacks Risk assessment in emergencies MEV 610003 Dr. C.J.W. Twenhöfel ERFRAD MEV 609002 Drs. Ing. N.J.C. van Belle
From sub acute to acute response
Clinical toxicology MEV 660001 Prof. Dr. J. Meulenbelt
Theme: INF
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Modelling CIb 210026 Dr. H. Grundmann Modelling the future of MRSA in NL
CIb 210036 Dr. J. Wallinga Tracking emerging epidemics CIb 210046 Dr. J. Wallinga Epidemic modelling of molecular data S CIb 210056 Mw. Dr. M. E.E.
Kretzschmar
Chlamydia positivity and prevalence
Immunology CIb 230426 Mw Dr. A.M. Buisman
Memory immunity
CIb 230146 Mw Dr. B. Pinelli2
Ortiz
Immunomodulation by helminth molecules
S CIb 230166 Mw Dr. B. Pinelli Ortiz
Zoonotic helminth infections and allergy
VGC 230406 Dr. C.M. Janssen Host-response to RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
CIb 230416 Dr. R.S. Van Binnendijk
Immune pathways in vaccination
Genomics CIb 230136 Dr. D. v. Soolingen
Whole-genome analysis of M. tuberculosis
CIb 230436 Dr. A.J. King Microarrays to map pertussis adaptation CIb 230446 Dr. F.R. Mooi B. pertussis adaptation to vaccination
S CIb 330116 Dr. H. Sprong Ticks: Trojan horses with new surprises INF - other S CIb 230156 Dr. E. Duizer Transmission intervention strategies
S CIb V/330274 Dr. A. M. Roda Husman
VITAL: foodborn viruses
Bold = new projects started in 2008, of which 2 did not really fit in with the subprogrammes.
Theme: CIL
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Modelling chronic diseases
VenZ 260146 Mw. Dr. Ir. W.M.M. Verschuren
Primary prevention research on cardiovascular diseases and diabetes
VenZ 210116 Dr. S.D. Mylius Adaptable chronic diseases modelling VenZ 260166 Mw. Dr. P.C.A.
Droomers
Modelling SES disparities in health
VGC 350040 Dr. Ir. J. Hoekstra Modelling health effects of nutrition Healthy ageing VenZ 206156 Dr.Ir. W.J.E.
Bemelmans
Healthy ageing: overweight/underweight
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
VGC 340020 Dr. M.E.T. Dollé Healthy ageing: gene diet interactions Quality of care VenZ 260116 Dr. G.P. Westert Health system performance Neth and CAN
C VenZ 270156 Dr. J.S. de koning Hospital performance measurement
VenZ 270116 Dr. C.H. van Gool Are diseases becoming less disabling?
Economic evaluations
VenZ 260176 Dr. T.L. Feenstra Communicating uncertainty in econ evals*
C VenZ 260186 Drs. G. A. de Wit Future unrelated medical costs Other VGC 350020 Dr. H.B. Bueno de
Mesquita
Primary prevention research on obesity, cancer and ageing
VenZ 270126 Mw. Dr. A.J. Schuit
Knowledge transfer in public health
VenZ 260126 Mw. Dr. A.H. Wijga
Lifestyle from childhood to adolescence
VenZ 260136 Mw. Dr. A.H. Wijga
Chronic diseases in childhood*
VenZ 270146 Mw. Dr.Ir. F. H.G.M. Hoeymans
Validation of data from general practise registries
C VenZ 270176 Mw. Dr. Ir. F. H.G.M. Hoeymans
Preparatory study for a national survey of primairy care
Theme: MFF
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Not applicable VGC 340040 Dr. Ir. R.J. Vandebriel
Chronic drug use and autoimmunity
VGC 350030 Dr. Ing. H.J. v. Kranen
The food pharma interface
VGC 370020 Drs. D. A. v. Riet-Nales MAGIC VGC 360010 Mw. Dr. S.W.J. Janssen Farmaco-economie VGC 360020 Dr. M.H.N. Hoefnagel Immunogeniteit eiwitgeneesmiddelen VGC 370010 Dr. D.M. Barends Riskred S VGC 370030 Dr. D.M. Barends BIOTHREE
Theme: EQH
Programme Division Project nr.
Project leader Title
Risk assessment MEV 607001 Dr. L. Posthuma EIA: environmental impact assessment MEV 607002 Prof. Dr. A.M.
Breure
RICIERA: research cooperation in ecological risk assessment
MEV 601001 Dr. T.G.Vermeire ITS: integrated testing strategies MEV 630006 Mw. Drs. C.M.A.G.
van Wiechen
SMARAGHT: small area health analyses, a geographic toolkit
MEV 610002 Dr. H. Slaper COURSE: climate and ozone change effects Interface risk
assessment and EHIA
MEV 610001 Dr. H. Bijwaard MIRACLE: modelling ionizing radiation and cancer for low dose effects
Environmental Health impact assessment
MEV 630001 Prof. Dr. Ir. E. Lebret
IRAS: environmental health collaboration
MEV 630002 Mw. Dr. N. Janssen
RAPTES: risks of airborne particles
MEV 630003 Prof. Dr. Ir. E. Lebret
VAMPHIRE: versatile assessment methodology project for health impacts and risks in the environment
MEV 630004 Mw. Dr. A. B. Knol IQARUS: uncertainty in environmental BOD
MEV 630005 Dr. R. van Poll PACEHR: perception, appraisal and communication of enviironmental risks Measurement
methods
MEV 680001 Dr. Ir. W.A.J. van Pul
NITROGEN: Relating groundwater + air quality for N
MEV 680002 Dr. A. Apituley CESAR: climate and air quality monitoring MEV 680003 Drs. D.P.J. Swart AQURES: air quality and remote sensing C MEV 680004 Dr. J. Jabben NOISE: improving noise exposure assessments
Annex 2 Papers from SOR projects in 2008
• Listed are scientific papers published or accepted in international peer-reviewed journals • RIVM staff is printed in bold; papers with RIVM staffers as their first, second and/or last
author are marked with a checkmark (√)
• The list inclused theses related to SOR projects • For project titles, see Annex 1
RPC, S/230126, Proteomics for population screening
√ Hofhuis A ; Reimerink J ; Reusken C ; Scholte EJ ; Boer AD ; Takken W ; Koopmans M The hidden passenger of lucky bamboo: do imported aedes albopictus mosquitoes cause dengue virus transmission in the Netherlands?
Vector Borne Zoon Dis, accepted
RPC, S/260196, Effective use performance indicators
√ Vos M de ; Graafmans W ; Kooistra M ; Meijboom B ; Voor P van der ; Westert G Using quality indicators to improve hospital care: a review of the literature
Int J Qual Health Care, accepted
RPC, S/270136, Getting.Better.nl
√ Ossebaard HC
Happy flow: in pursuit of a consumers? J Med Internet Res, accepted
RPC, S/340030, Nanotechnology, potential risks
Barnes CA ; Elsaesser A ; Arkusz J ; Smok A ; Palus J ; Lesniak A ; Salvati A ; Hanrahan JP ; Jong WH de ; Dziubaltowska E ; Stepnik M ; Rydzynski K ; McKerr G ; Lynch I ; Dawson KA ; Howard CV
Reproducible comet assay of amorphous silica nanoparticles detects no genotoxiciy Nano Lett 2008; 8(9):3069-74
RPC, S/340050, Alternatives for animal testing
√ Kesteren PCE van ; Beems RB ; Luijten M ; Robinson J ; Vries A de ; Steeg H van
DNA repair-deficient Xpa/p53 knockout mice are sensitive to the non-genotoxic carcinogen cyclosporine A: escape of initiated cells from immunosurveillance?
Carcinogenesis 2009; 30(3):538-43
RPC, S/350010, Methods for dietary exposure assessment
√ Fransen HP ; Ock M
Indices of diet quality
Schickenberg B ; Assema P van ; Brug J ; Verkaik-Klosterman J ; Ocké MC ; Vries NK
Replacing foods high in saturated fat by low-saturated fat alternatives: a computer simulation of the potential effects on reduction of saturated fat consumption
Br J Nutr, accepted
ERF, S/610003, ERFRAD
√ Heuvelink GBM ; Jiang Z ; Bruin S de ; Twenhöfel CJW Optimization of mobile radioactivity monitoring networks Int J Geographical Information Sci, accepted
Hiemstra P ; Pebesma EJ ; Twenhöfel CJW ; Heuvelink GBM
Real-time automatic interpolation of ambient gamma dose rates from the Dutch Radioactivity Monitoring Network Computers & Geosciences, accepted
√ Hiemstra PH ; Pebesma EJ ; Twenhöfel CJW ; Heuvelink GBM
Automatic real-time interpolation of radiation hazards: prototype and system architecture considerations Int J Spatial Data Infrastruct Res 2008; 3(1):58-72
ERF, S/630007, Rapid assessments after disasters
√ Bongers S ; Janssen NAH ; Reiss B ; Grievink L ; Lebret E ; Kromhout H
Challenges of exposure assessment for health studies in the aftermath of chemical incidents and disasters J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 2008; 18(4):341-59
ERF, S/660001, Research cooperation in human toxicology
√ Hunault CC ; Mensinga TT ; Bocker KBE ; Schipper CMA ; Leenders MEC ; Vries I de ; Meulenbelt J Cognitive and psychomotor effects in males after smoking a combination of tobacco and cannabis containing up to 69 mg delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Psychopharmacology 2009; accepted
√ Hunault CC ; Mensinga TT ; Vries I de ; Kelholt-Dijkman HH ; Hoek J ; Kruidenier M ; Leenders MEC ;
Meulenbelt J
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) serum concentrations and pharmacological effects in males after smoking a combination of tobacco and cannabis containing up to 69 mg THC
Psychopharmacology 2008; 201(2):171-81
INF, S/210036, Tracking emerging epidemics
√ Heijne JCM ; Teunis P ; Morroy G ; Wijkmans C ; Oostveen S ; Duizer E ; Kretzschmar M ; Wallinga J
Enhanced hygiene measures and norovirus transmission during an outbreak Emerg Infect Dis 2009; 15(1):24-30
Mossong J ; Hens N ; Jit M ; Beutels P ; Auranen K ; Mikolajcyk R ; Massari M ; Salmaso S ; Scalia Tomba G; Wallinga J ; Heijne J ; Sadkowska-Todys M ; Rosinska M ; Edmunds WJ
Social contacts and mixing patterns relevant to the spread of infectious diseases PloS Med 2008; 5(3):e74
A simple explanation for the low impact of border control as a countermeasure to the spread of an infectious disease
Math Biosci 2008; 214(1-2):70-2
INF, S/210046, Epidemic modelling of molecular data
√ Boot HJ ; Cremer J ; Koedijk FDH ; Ballegooijen WM van ; Op de Coul ELM
Improved tracing of hepatitis B virus transmission chains by phylogenetic analysis based on C region sequences
J Med Virol 2008; 80(2):233-41
INF, S/210056, Chlamydia positivity and prevalence
√ Low N ; Heijne JCM ; Kretzschmar M
Use of mathematical modelling to inform Chlamydia screening policy decisions J Infect Dis 2009; 199(5):767-8
INF, S/230406, Host-response to RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus)
√ Pennings JLA ; Kimman TG ; Janssen R
Identification of a common gene expression response in different lung inflammatory diseases in rodents and macaques
PLoS ONE 2008; 3(7):e2596
√ Siezen CL ; Bont L ; Hodemaekers HM ; Ermers MJ ; Doornbos G ; Slot R van 't ; Wijmenga C ; Kimpen
JC ; Houwelingen HC van ; Kimman TG ; Hoebee B ; Janssen R
Genetic susceptibility to RSV bronchiolitis in preterm children is associated with airway remodelling genes and innate immune genes
Ped Infect Dis J, accepted
INF, S/230436, Microarrays to map pertussis adaption
√ King AJ ; Gorkom T van ; Pennings JLA ; Heide HGJ van der ; He Q ; Diavatopoulos D ; Heuvelman K Gent M van ; Leeuwen K van ; Mooi FR
Comparative genomic profiling of Dutch clinical Bordetella pertussis isolates using DNA microarrays: identification of genes absent from epidemic strains
BMC Genomics 2008; 9:311
Stenger RM ; Poelen MCM ; Moret EE ; Kuipers B ; Bruijns SCM ; Hoogerhout P ; Hijnen M ; King AJ ;
Mooi FR ; Boog CJP ; Els CACM van
Immunodominance in mouse and human CD4+ T-cell responses specific for the Bordetella pertussis virulence factor P.69 pertactin
Infect Immun 2009; 77(2):896-903
CIL, S/260186, Future unrelated medical costs
√ Feenstra TL ; Baal PHM van ; Gandjour A ; Brouwer WBF
Future costs in economic evaluation. A comment on Lee [Reply] J Health Econ 2008; 27(6):1645-9
√ Rappange DR ; Baal PHM van ; Exel NJA ; Feenstra TL ; Rutten FFH ; Brouwer WBF
Unrelated medical costs in life-years gained: should they be included in economic evaluations of healthcare interventions?
Pharmacoeconomics 2008; 26(10):815-30
CIL, S/270146, Validation of data from general practise registries
√ Dungen C van den ; Hoeymans N ; Gijsen R ; Akker M van den ; Boesten J ; Brouwer H ;
Smeets H ; Venn WJ van der ; Verheij R ; Waal M de ; Schellevis F ; Westert G What factors explain the differences in morbidity estimations among general practice registration networks in the Netherlands? A first analysis
Eur J Gen Pract 2008; 14(suppl 1):53-62
CIL, S/340020, Healthy ageing: gene diet interactions
√ A DL van der ; Rovers MM ; Grobbee DE ; Marx JJM ; Waalen J ; Ellervik C ; Nordestgaard
BG ; Olynyk JK ; Mills PR ; Shepherd J ; Grandchamp B ; Boer JMA ; Caruso C ; Arca M ; Meyer BJ ; Schouw YT van der
Mutations in the HFE gene and cardiovascular disease risk. An individual patient data meta- analysis of 53880 subjects
Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2008; 1:43-50
Andressoo JO ; Weeda G ; Wit J de ; Mitchell JR ; Beems RB ; Steeg H van ; Horst GTJ van der ; Hoeijmakers JH
An Xpb mouse model for combined xeroderma pigmentosum and cockayne syndrome reveals progeroid features upon further attenuation of DNA repair
Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29(5):1276-90
√ Berg SW van den ; Jansen EHJ ; Kruijshoop M ; Beekhof PK ; Blaak E ; Kallen CJ van der
; Greevenbroek MM van ; Feskens EJM
Paraoxonase 1 phenotype distribution and activity differs in subjects with newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes (the CODAM Study)
Diabetic Med 2008; 25(2):186-93
Garcia AM ; Busuttil RA ; Calder RB ; Dollé MET ; Diaz V ; McMahan CA ; Bartke A ; Nelson J ; Reddick R ; Vijg J
Effect of Ames dwarfism and caloric restriction on spontaneous DNA mutation frequency in different mouse tissues
Mech Ageing Dev 2008; 129(9):528-33
√ Kuijsten A ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Boer JM ; Arts IC ; Kok FJ ; Veer P van 't ; Hollman PC
Plasma enterolignans are not associated with nonfatal myocardial infarction risk Atherosclerosis 2009; 203(1):145-52
√ Lu Y ; Dollé ME ; Imholz S ; Slot R van 't ; Verschuren WMM ; Wijmenga C ; Feskens EJ ; Boer JM Multiple genetic variants along candidate pathways influence plasma high-density lipoprotein
cholesterol concentrations J Lipid Res 2008; 49(12):2582-9 SOR-CIL 2008
Ouchida R ; Ukai A ; Mori H ; Kawamura K ; Dollé MET ; Tagawa M ; Sakamoto A ; Tokuhisa T ; Yokosuka T ; Saito T ; Yokoi M ; Hanaoka F ; Vijg J ; Wang JY
Genetic analysis reveals an intrinsic property of the germinal center B cells to generate A:T mutations
DNA repair 2008; 7(8):1392-8
Park JY ; Cho MO ; Leonard S ; Calder B ; Mian S ; Kim WH ; Wijnhoven S ; Steeg H van ; Mitchell J ; Horst GTJ van der ; Hoeijmakers J ; Cohen P ; Vijg J ; Suh Y
Homeostatic imbalance between apoptosis and cell renewal in the liver of premature aging Xpd-TTD mice
PLoS ONE 2008; 3(6):e2346
Schumacher B ; Pluijm I van der ; Moorhouse MJ ; Kosteas T ; Robinson AR ; Suh Y ; Breit TM ; Steeg H
van ; Niedernhofer LJ ; Ijcken W van ; Bartke A ; Spindler SR ; Hoeijmakers JHJ ; Hors GTJ van der ; Garinis
GA
Delayed and accelerated aging share common longevity assurance mechanism Plos Genetics 2008; 4(8):e1000161
CIL, S/350020, Primary prevention research on obesity, cancer and ageing
Besson H ; Ekelund E ; Luan J ; May AM ; Sharp S ; Travier N ; Agudo A ; Slimani N ; Rinaldi S ; Norat T ; Mouw T ; Rohrmann S ; Bergmann M ; Boeing H ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Boutron-Ruault MC ; Jacobson MU ; Overvad K ; Tjonneland A ; Halkjaer J ; Gonzalez C ;
Rodriguez L ; Sanchez MJ ; Dorronsoro M ; Barricarte A ; Navarro C ; Key T ; Spencer E ; Orfanos P ; Naska A ; Trichopoulou A ; Manjer J ; Hallmans G ; Lund E ; Palli D ; Agnoli C ; Vineis P ; Panico S ; Tumino R ;
Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Odysseos A ; Riboli E ; Wareham NJ ; Peeters PH
Association between physical activity and obesity across 9 European countries: a cross- sectional analysis in the EPIC-PANACEA study
Int J Obesity 2009; accepted
Capella G ; Pera G ; Sala N ; Agudo A ; Rico F ; El Giudicce G ; Plebani M ; Palli D ; Boeing H ; Bueno de
Mesquita HB ; Carneiro F ; Berrino F ; Vineis P ; Tumino R ; Panico S ; Berglund G ; Siman H ; Nyren O ;
Hallmans G ; Martinez C ; Dorronsoro M ; Barricarte A ; Navarro C ; Quiros JR ; Allen N ; Key T ; Bingham S ; Caldas C ; Linseisen J ; Nagel G ; Overvad K ; Tjonneland A ; Boshuizen HC ; Peeters PHM ; Numans ME ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Trichopoulou A ; Lund E ; Jenab M ; Kaaks R ; Riboli E ; Gonzalez CA
DNA repair polymorphisms and the risk of stomach adenocarcinoma and severe chronic gastritis in the EPIC-EURGAST study
Int J Epidemiol 2008; 37(6):1316-25
Crusius JBA ; Canzian F ; Capella G ; Pena AS ; Pera G ; Sala N ; Agudo A ; Rico F ; Giudice del ; Palli D ; Plebani M ; Boeing H ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Carneiro F ; Pala V ; Save VE ; Vineis P ; Tumino R ; Panico S ; Berglund G ; Manjer J ; Stenling R ; Hallmans G ; Martinez C ; Dorronsoro M ; Barricarte A ; Navarro C ; Quiros JR ; Allen N ; Key TJ ; Bingham S ; Caldas C ; Linseisen J ; Kaaks R ; Overvad K ; Tjonneland A ; Buchner FC ; Peeters PHM ; Numans ME ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Trichopoulou A ; Lund E ; Jenab M ; Rinaldi S ; Ferrari P ; Riboli E ; Gonzalex CA Cytokine gene polymorphisms and the risk of adenocarcinoma of the stomach in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
(EPIC-EURGAST)
Hung RJ ; McKay JD ; Gaborieau V ; Boffetta V ; Hashibe M ; Zaridze D ; Mukeria A ; Szeszenia-Dabrowska N ; Lissowska J ; Rudnai P ; Fabianova E ; Mates D ; Bencko V ; Foretova L ; Janout V ; Chen C ; Goodman G ; Field JK ; Liloglou T ; Xinarianos G ; Cassidy A ; McLaughlin J ; Liu G ; Narod S ; Krokan HE ; Skorpen F ; Bratt Elvestad M ; Hveem K ; Vatten L ; Linseisen J ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Vineis P ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Lund E ; Martinez C ; Bingham S ; Rasmuson T ; Hainaut P ; Riboli E ; Ahrens W ; Benhamou S ; Lagiou P ; Trichopoulos D ; Holcatova I ; Merletti F ; Kjaerheim K ; Agudo A ; Macfarlane G
; Talamini R ; Simonato L ; Lowry R ; Conway DI ; Znaor A ; Healy C ; Zelenika D ; Boland A ; Delepine M ; Foglio M ; Lechner D ; Matsuda F ; Blanche H ; Gut I ; Heath S ; Lathrop M ; Brennan P
A susceptibility locus for lung cancer maps to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes on 15q25 Nature 2008; 452(7187):633-7
Jenab M ; McKay JD ; Ferrari P ; Biessy C ; Laing S ; Munar GM ; Sala N ; Crusius JB ; Overvad K ; Jensen MK ; Olsen A ; Tjonneland A ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Boutron-Ruault MC ; Kaaks R ; Linseisen J ; Boeing H ; Bergmann MM ; Trichopoulou A ; Georgila C ;
Psaltopoulou T ; Mattiello A ; Vineis P ; Pala V ; Palli D ; Tumino R ; Numans ME ; Peeters PH ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Lund E ; Ardanaz E ; Sanches MJ ; Dorronsoro M ; Sanchez CN ; Quiros JR ; Hallmans G ; Stenling R ; Manjer J ; Regner S ; Key T ; Bingham S ; Khaw KT ; Slimani N ; Rinaldi S ; Boffetta P ; Carneiro F ; Riboli E ; Gonzalez C
CDH1 gene polymorphisms, smoking, Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric cancer in the European Prospective Investigation into
Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-EURGAST) Eur J Cancer 2008; 44(6):774-80
Johansson M ; Appleby PN ; Allen NE ; Travis RC ; Roddam AW ; Egevad L ; Jenab M ; Rinaldi S ; Kiemeney LA ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Vollset SE ; Ueland PM ; Sanchez MJ ; Quiros JR ; Gonzalez CA ; Larranaga N ; Chirlaque MD ; Ardanaz E ; Sieri S ; Palli D ; Vineis P ; Tumino R ; Linseisen J ; Kaaks R ; Boeing H ; Pischon T ; Psaltopoulou T ; Trichopoulou A ; Trichopoulos D ; Khaw KT ; Bingham S ; Hallmans G ; Riboli E ; Stattin P ; Key TJ
Circulating concentrations of folated and vitamin B12 in relation to prostate cancer risk: results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition study
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008; 17(2):279-85
√ Kuijsten A ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Boer JM ; Arts IC ; Kok FJ ; Veer P van 't ; Hollman PC
Plasma enterolignans are not associated with nonfatal myocardial infarction risk Atherosclerosis 2009; 203(1):145-52
√ Kuijsten A ; Hollman PCH ; Boshuizen HC ; Buijsman MNCP ; Veer P van 't ; Kok FJ ; Arts ICW ; Bueno
de Mesquita HB
Plasma enterolignan concentrations and colorectal cancer risk in a nested case-control study Am J Epidemiol 2008; 167(6):734-42
McKay JD ; Hung RJ ; Gaborieau V ; Boffetta P ; Chabrier A ; Byrnes G ; Zaridze D ; Mukeria A ; Szeszenia-Dabrowska N ; Lissowska J ; Rudnai P ; Fabianova E ; Mates D ; Bencko V ; Foretova L ; Janout V ; McLaughlin J ; Shepherd F ; Montpetit A ; Narod S ; Krokan HE ; Skorpen F ; Elvestad MD ; Vatten L ; Njolstad I ; Axelsson T ; Chen C ; Goodman G ; Barnett M ; Loomis MM ; Lubiski J ; Matyjasik J ; Lener M ; Oszutowska D ; Field J ; Liloglou T ; Xinaranos G ; Cassidy A ; Zelenika D ; Boland A ; Delepine M ; Foglio M ; Lechneer D ; Matsuda F ; Blanche H ; Gut I ; Heath S ; Lathrop M ; Brennan P ; Vineis P ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Palli D ; Tumino R ; Krogh V ; Panico S ; Gonzalez CA ; Ramon Quiros J ; Martinez C ;
Navarro C ; Ardanaz E ; Larraaga N ; Kham KT ; Key T ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Peeters PHM ; Trichopoulou A ; Linseisen J ; Boeing H ; Hallmans G ; Overvad K ; Tjonneland A ; Kumle M ; Riboli E Lung cancer susceptibility locus at 5p15.33
Nature Genetics 2008; 40(12):1404-6
√ Menvielle G ; Boshuizen H ; Kunst AE ; Dalton SO ; Vineis P ; Bergmann MM ; Hermann S ; Ferrari P ; Raaschou-Nielsen O ; Tjonneland A ; Kaaks R ; Linseisen J ; Kosti M ;
Trichopoulou A ; Dilis V ; Palli D ; Krogh V ; Panica S ; Tumino R ; Buchner FL ; Gils CH van ; Peeters PH ; Braaten T ; Gram IT ; Lund E ; Rodriguez L ; Agudo A ; Sanchez MJ ; Tormo MJ ; Ardanaz E ; Manjer J ; Wirfalt E ; Hallmans G ; Rasmuson T ; Bingham S ;
Khaw KT ; Allen N ; Key T ; Boffetta P ; Duell EJ ; Slimani N ; Gallo V ; Riboli E ; Bueno de Mesquita HB The role of smoking and diet in explaining educational inequalities in lung cancer incidence
J Nat Cancer Inst 2009; accepted
Nothlings U ; Murphy SP ; Wilkens LR ; Boeing H ; Schulze MB ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Michaud D ; Roddam A ; Rohrmann S ; Tjonneland A ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Trichopoulou A ; Sieri S ; Rodriguez L ; Ye W ; Jenab M ; Kolonel LN
A food pattern that is predictive of flavonol intake and risk of pancreatic cancer Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88(6):1653-62
Pischon T ; Boeing H ; Hoffman K ; Bergmann M ; Schulze PH ; Overvad MD ; Schouw YT van der ; Spencer E ; Moons KGM ; Tjonneland A ; Halkjaer J ; Jensen MK ; Stegger J ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Boutron-Ruault MC ; Chajes V ; Linseisen J ; Kaaks R ; Trichopoulou A ; Trichopoulos D ; Barnia C ; Sieri S ; Palli D ; Tumino R ; Vineis P ; Panico S ; Peeters PHM ; May AM ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Duijnhoven FJB van ; Hallmans G ; Weinehall L ; Manjer J ; Hedblad B ; Lund E ; Agudo A ; Arriola L ; Barricarte A ; Navarro C ; Martinez C ; Quiros JR ; Key T ; Phil D ; Bingham S ; Khaw KT ; Chir B ; Boffetta P ; Jenab M ; Ferrari P ; Riboli E General and abdominal adiposty and risk of death in Europe
New England J Med 2008; 359(2):2105-20
Rinaldi S ; Rohrmann S ; Jenab M ; Biessy C ; Sieri S ; Palli D ; Tumino R ; Mattiello A ; Vineis P ; Nieters A ; Linseisen J ; Pischon T ; Boeing H ; Hallmans G ; Palmqvist R ; Manjer
J ; Wirfalt E ; Crowe FL ; Khaw KT ; Bingham S ; Tjonneland A ; Olsen A ; Overvad K ; Lund E ; Skeie G ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Boutron-Ruault MC ; Lauzon-Guillain B de ; Ardanaz E ; Jakszyn P ; Quiros JR ; Chirlaque MD ; Sanchez MJ ; Dorronsoro M ; Trichopoulou A ; Lagiou P ; Trichopoulos D ; Bueno de
Mesquita HB ; Duijnhoven FJB van ; Peeters PHM ; Slimani N ; Ferrari P ; Byrnes GB ; Riboli E ; Kaaks R
Glycosylated hemoglobin and risk of colorectal cancer in men and women, the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2008; 17(11):3108-15
Saadatian-Elahi M ; Slimani N ; Chajes C ; Jenab M ; Goudable J ; Biessy C ; Ferrari P ; Byrnes G ; Autier P ; Peeters PHM ; Ocké M ; Bueno de Mesquita HB ; Johansson I ; Hallmans G ; Manjer J ; Wirfalt E ; Gonzalez CA ; Navarro C ; Martinez C ; Amiano P ; Rodriguez Suarez L ; Ardanaz E ; Tjonneland A ; Halkjaer J ; Overvad K ; Uhre Jakobsen M ; Berrino F ; Pala V ; Palli D ; Tumino R ; Vineis P ; Santucci de Magistris M ; Spencer EA ; Crowe FL ; Bingham S ; Khaw KT ; Linseisen J ; Rohrmann S ; Boeing H ; Noethlings U ; Standahl Olsen K ; Skeie G ; Lund E ; Trichopoulou A ; Oustoglou E ; Clavel-Chapelon F ; Riboli E
Plasma phospholipid fatty acid profiles and their association with food intakes: resulst from a cross-sectional study within the European
Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 89(1):331-46
√ Vrieling A ; Verhage BAJ ; Duijnhoven FJB van ; Jenab M ; Overvad K ; Tjonneland A ; Olsen A ;
Clavel-Chapelon F ; Boutron-Ruault MC ; Kaaks R ; Rohrmann S ; Boeing H ; Nothlings U ; Trichopoulou A ; John T ; Dimosthenes Z ; Palli D ; Sieri S ; Mattiello A ; Tumino R ; Vineis P ; Gils CH van ; Peeters PHM ; Engeset D ; Lund E ; Rodriguez Suarez L ; Jakszyn P ; Larranaga N ; Sanchez MJ ; Chirlaque MD ; Ardanaz E ; Manjer J ; Lindkvist B ; Hallmans G ; Ye W ; Bingham S ; Khaw KT ; Roddam A ; Key T ; Boffetta P ; Duell EJ ; Michaud DS ; Riboli E ; Bueno de Mesquita HB
Fruit and vegetable consumption and pancreatic cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
Int J Cancer 2009; 124(8):1926-34
CIL, S/350040, Modelling health effects of nutrition
√ Jong N de ; Ros MM ; Ocké MC ; Verhagen H
A general postlaunch monitoring framework for functional foods tested with the phytosterol/stanol case Trends Food Sci Technol 2008; 19(10):535-45
MFF, S/370030, BIOTHREE
√ Arnal J ; Gonzalez-Alvarez I ; Bermerjo M ; Amidon GL ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ; Dressman JB ; Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Aciclovir J Pharm Sci 2008; 97(12):5061-73
√ Becker C ; Dressman JB ; Amidon GL ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ;
Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Ethambutol dihydrochloride J Pharm Sci 2008; 97(4):1350-60
√ Becker C ; Dressman JB ; Amidon GL ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ;
Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Pyrazinamide J Pharm Sci 2008; 97(9):3709-20
√ Becker C ; Dressman JB ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ; Barends DM Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Rifampicine
J Pharm Sci 2009, accepted
Benet LZ ; Amidon GL ; Barends DM ; Lennernaes H ; Polli JE ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky SA ; Yu LX The use of BDDCS in classifying the permeability of marketed drugs
Pharm Res 2008; 25(3):483-8
√ Chuasuwan B ; Binjesoh V ; Polli JE ; Zhang H ; Amidon GL ; Junginger HE ; Midha KK ; Shaw VP ; Stavchansky S ; Dressman JB ; Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Diclofenac sodium and Diclofenac potassium
√ Granero GE ; Longhi MR ; Becker C ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ; Dressman JB ; Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Acetazolamide J Pharm Sci 2008; 97(9):3691-9
√ Grube S ; Langguth P ; Junginer HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ; Dressman JB ;
Barends DM
Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Quinidine sulfate J Pharm Sci 2009, accepted
√ Stosik AG ; Junginger HE ; Kopp S ; Midha KK ; Shah VP ; Stavchansky S ; Dressman JB ; Barends DM Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms: Metoclopramide hydrochloride J Pharm Sci 2008; 97(9):3700-8
EQH, S/607001, EIA: environmental impact assessment
Brack W ; Apitz SE ; Borchard D ; Brils J ; Cardoso AC ; Foekema EM ; Gils J van ; Jansen B ; Harris M ; Hein M ; Heise S ; Hellsten S ; Maagd GJ de ; Muller D ; Panov VE ; Posthuma L ;
Quevauviller P ; Verdonschot PFM ; Ohe PC von der
Towards a holistic and risk-based management of European river basis Integr Environ Assess Manage, accepted
√ Hauck M ; Huijbregts MAJ ; Armitage JM ; Cousins IT ; Ragas AMJ ; Meent D van de
Model and input uncertainty in multi-media fate modelling: benzo[a]pyrene concentrations in Europe Chemosphere 2008; 72(6):959-67
Kapo KE ; Burton GA ; Zwart D de ; Posthuma L ; Dyer SD
Quantitative lines of evidence for screening-level diagnostic assessment of regional fish community impacts: a comparison of spatial database evaluation methods
Environ Sci Technol 2008: 42(24):9412-8
√ Mulder C ; Hollander HA den ; Hendriks AJ
Aboveground herbivory shapes the biomass distribution and flux of soil invertebrates PLoS ONE 2008; 3(10):e3573
√ Reuman DC ; Mulder C ; Raffaelli D ; Cohen JE
Three allometric relations of population density to body mass: theoretical integration and empirical tests in 149 food webs
Ecol Lett 2008; 11(11):1216-28
√ Wal A van der ; Bloem J ; Mulder C ; Boer W de
Relative abundance and activity of melanized hyphae in different soil ecosystems Soil Biol Biochem 2009; 41(2):417-9
√ Zelm R van ; Huijbregts MAJ ; Posthuma L ; Wintersen A ; Meent D van de
Pesticide ecotoxicological effect factors and their uncertainties for freshwater ecosystems Int J Life Cycle Assess 2009; 14(1):43-51