Opgeloste Examenvragen Digital
Organisation
De cursusdienst van de faculteit Toegepaste
Economische Wetenschappen aan de Universiteit
Antwerpen.
Op het Weduc forum vind je een groot aanbod van samenvattingen, examenvragen, voorbeeldexamens en veel meer, bijgehouden door je medestudenten.
Opgeloste Examenvragen Digital Organisation
1. What are the 4 types of information systems, fully explained: Transaction processing systems
Systems that typically automate recurring operational activities in business processes – Serve operational managers and staf
– Perform and record daily routine transactions necessary to conduct business Examples: sales order entry, payroll, shipping, reception in the hotel:
complete the information of your booking in the system
– Allow managers to monitor status of operations and relations with external environment
– Serve predefined, structured goals and decision making Management Information Systems
• Serve middle management
• Provide reports on firm’s current performance, based on data from TPS
• Provide answers to routine questions with predefined procedure for answering them • Typically, have little analytic capability
Decision support systems
• Serve middle management
• Support non-routine decision making
– Example: What is the impact on production schedule if December sales doubled?
• May use external information as well TPS / MIS data • Model driven DSS
– Voyage-estimating systems • Data driven DSS
– Intrawest’s marketing analysis systems Executive Support Systems
• Support senior management • Address non-routine decisions
– Requiring judgment, evaluation, and insight
• Incorporate data about external events (e.g., new tax laws or competitors) as well as summarized information from internal MIS and DSS
• Example: Digital dashboard with real-time view of firm’s financial performance 2. What’s IT outsourcing? In which conditions is this useful and what are the cost
components?
Outsource of-shore: I’m not going to develop myself (very expensive): outsource everything: for example, move it to India because the cost is much lower (good developers in India) Outsource the development of our application to other cheap countries: risk? Cost-efficient but the risk is that the Indian people have an other understanding than what you are trying to say: manage this relationship
Nearshore: go to closer countries: such as Poland, Hungary, Spain and Portugal: cheaper but makes the risk of the other people having an other understanding lower
Onshore: do it in Belgium near to the company Cost
Many firms underestimate the costs for identifying and evaluating vendors of information technology services, for transitioning to a new vendor, for improving internal software development methods to match those of outsourcing vendor, and for monitoring vendors to make sure they are fulfilling their contractual obligations. Also handling traveling expenses. Outsourcing ofshore incurs additional costs for coping with cultural diferences that drain productivity and dealing with human resources issues, such as terminating or relocating domestic employees. All of these hidden costs undercut some of the anticipated benefits from outsourcing.
3. Model of porter and the influence from the internet, do the threats and opportunities increase or decrease?
- Traditional competitors - New market entrants
- Substitute products and services - Customers
- Suppliers
The Internet’s Impact on Competitive Advantage • Transformation or threat to some industries
– Examples: travel agency, printed encyclopedia, media • Competitive forces still at work, but rivalry more intense • Universal standards allow new rivals, entrants to market
• New opportunities for building brands and loyal customer bases
Information is available to everyone, so the internet raises the bargaining power of the customers. Customers can quickly find the company with the lowest prices. Profits have because of this dampened. Internet has nearly destroyed some industries and has severely threatened more. Internet is ‘’transforming’’ entire industries, forcing firms to change how they do business. created entirely new markets: formed the basis for thousands of new products, services, and business models.
4. E-business?
Systems that are trying to automate our primary and secondary business processes: use of digital technology and Internet to drive major business processes
5. Explain CRM for sales, marketing, customer service, link between ERP and CRM? Sales force automation (SFA)
It helps sales staf increase productivity by focusing sales eforts on the most profitable customers, those who are good candidates for sales and services. SFA modules provide sales, prospect and contact information, production information, product configuration capabilities and sales quote generation capability. SFA modules enable sales, marketing, and shipping departments to share customer and prospect information easily. Reduces cost of acquiring new customers and retaining old ones.
Customer service models in CRM systems provide information and tools to increase the efficiency of call centres, help desks, and customer support staf. They have capabilities for assigning and managing customer service requests. When the customer’s data is already in the system, any service representative can handle the customer relationship. This helps call-centres handle more calls per days and decrease the duration of each call. CRM systems may also include web-based self-service capabilities: the company website can be set up to provide inquiring customers personalized support information as well as the option to contact the customer service staf by phone for additional assistance.
Marketing
Support direct-marketing campaigns by providing capabilities for capturing prospect and customer data, for providing product and service information, for qualifying leads for
targeted marketing and for scheduling and tracking direct marketing mailings or e-mail. Tools for analysing marketing and customer data; identifying profitable and unprofitable
customers, design products and services.
Cross-selling: marketing of complementary products to customers. CRM tools also help firm manage and execute marketing campaigns at all stages, form planning to determine the rate of success for each campaign.
Link wit ERP:
• CRM systems
A lot of venders that sell CRM-tools to support this custom care business process: inside SAP, Microsoft, salesfore.com: capture customer data: create an unique single view on the customer
– Capture and integrate customer data from all over the organization – Consolidate and analyze customer data
– Distribute customer information to various systems and customer touch points across enterprise
– Provide single enterprise view of customers
6. General controls vs application controls, what’s the link with SOX? Information Systems Controls
• General controls
Govern design, security, and use of computer programs and security of data files in general throughout organization (organizational things you are going to organise that apply to all information system)
Software controls, hardware controls, computer operations controls, data security controls, system development controls, administrative controls, • Application controls
Controls unique to each computerized application Input controls, processing controls, output controls SOX
CEO/CFO has to guarantee in person that all the facts in the financial report are accurate and correct if it’s not accurate the fine is not a fine on the revenue but the CEO/CFO goes to jail Technology helps to keep it accurate and keeps it protected so other people don’t have access
7. It’s doesn’t matter but business processes do ‘’It doesn’t matter’’ – Carr 2003
Parallel between IT and electricity namely the first companies who started with electricity had a huge advantage = unique
But what happened to the electricity as an asset? It has become a commodity: we try to use it at a low cost: same is happening to IT
We do not agree: there is a part in IT that has commodities: examples: laptop, iPhone, printer (outsource this kind of IT)
‘’Business processes do matter’’ – Carr
Business technologies can really impact the businesses, for an example as bol.com IT does matter
8. What are the 5 goals goals that firms try to achieve while investing in IT? Firms invest heavily in information systems to achieve six strategic business objectives:
Operational excellence
Understand how your business process is operated and making it as cost efficient and efective as possible
The fulfilment tac: when someone orders a package it requires a lot of technology to get it in time by the customer
Retail: fully automated supply chain: how much milk is still available in the store and do we have to supply more now?
New products, services, and business models
iTunes has turned the music industry down (highly impacted) you can now legally stream music It is no longer physical (CD)
Uber: taxi industry Air bnb: hotel industry
Customer and supplier intimacy
Hotel chains who try to capture your data and preferences, they will make sure that in your room your favourite song is playing and the temperature is exact what you like: fully
automated
KLM: flying with airplanes has become a commodity, you chose your flight based on the price. It is important to increase customer satisfaction
KLM Invested a lot in social media, when u lose your baggage you can put your complaint on Facebook or twitter and KLM guarantees that within one hour you are contacted with a solution
= creating a unique facility, considering this when choosing a flight Improved decision making
A chain of bakers: educate the bakers so that they are up to date with the health regulations Bakery battle app: game on health regulations, security regulations
Bakers that had a bad score put together with bakers that had a good score so they could work together and learn from each other
Competitive advantage
Continuously improving experience: to be competitive: have an advantage
First bank internet All the banks become internet bank First bank Mobile bank All the banks become mobile banks
Very competitive industry: what is going to happen next? Survival
Firms have to keep up with other companies in order to be competitive 9. Pure-play company? Click and mortar company?
Click and morter company is derived from the world brick and morter company: a company like JBC or Adidas, as long as these players were not selling their products online they were bricks and mortars company’s: right now they are click and mortar companies because they have an online shop
Pure play company is a company that has always been virtual like google/iTunes: it never had a physical store
10. Diference between operational and analytic CRM? Operational CRM
In support of the real running customer care activities: how do you do loyalty programs? About the opartions of crm, doing the customer care
Customer-facing applications Sales force automation
Call center and customer service support Marketing automation
Analytical CRM
Use the same database as operational CRM: they are going to generate reports out of it: get the management information out
Based on data warehouses populated by operational CRM-systems and customer touch points
Analyzes customer data (OLAP, data mining, etc.) Customer lifetime value (CLTV)
What did we already spend on this client? What did we already earn from this client in terms of sales and profits? Hopely positive: earned more than spend on this client
11. How can a company reduce complaints? What’s an ethical motive for clients to complain? (niet zeker of dit in cursus staat?)
First searching clients who are the displeased, helping this clients first. Than going further working as an ‘’triage system’’. There are always some clients lost, don’t put time and efort in this clients
The proces is more important for clients, they just want to have good treatment. If the enddproduct isn’t really what theyt expected they are less likely to complain. One time clients you can best give money in return for the bad product.
12. Agent theory and transaction theory: why outsource IT according transaction theory? Economic impact: Transaction Cost Theory
Transaction cost
= costst that organziations have to make when they want to require goods and services in the market
• Firms seek to economize on transaction costs (the costs of participating in markets) – Vertical integration, hiring more employees, buying suppliers and distributors • IT lowers market transaction costs, making it worthwhile for firms to transact with
other firms rather than grow the number of employees (eg. Dell)
Become a vertical integrated company: do everything yourself: you have less transaction costs: you can become a bigger company: IT can lower the transaction cost
Because of IT it can become more efficient because IT makes it easier to do transactions in the market
IT is reducing the transaction cost = economic impact Economic impact: Agency Theory
= owner of the company and the agent that works for the company
= costs that you have to make as an owner to control the agent: agent will maybe not work by himself for your best interest
A big company has a lot more agency costs than a small company
• Firm is nexus of contracts among self-interested parties requiring supervision • Firms experience agency costs (the cost of managing and supervising) which rise as
firm grows
• IT can reduce agency costs, making it possible for firms to grow without adding to the costs of supervising, and without adding employees
Impact of IT?
Agency cost can go down because of the use of technology, systems that give you more information at hand, in real time, makes it for the owner much more efficient to control your workers
Force people to work in a specific way trough an information system Agency cost reduces
13. Disintermediation? Re-intermediation? What makes e-commerce unique compared to traditional markets?
Disintermediation: in the past if you wanted to buy an airplane ticket you needed to go to the shop (retailer) but now there is disintermediation: disappearing of the intermediate players in the chain: it becomes more interesting for the customer because all the intermediaries want to put something in the pocket (lower price)
Re-intermediation: the situation where new players come up and try to find their space their in-between
For example: cheaptickets.nl
Contra-intermediation: for example: opodo.com: has been created by a consortium of airplane companies who have organised themselves as the intermediate player: manufacturer has control over the player
Why E-commerce Is different
E-commerce has grown dramatically, because it has some features that guarantee success • Ubiquity
– Marketspace is virtual (not physical) You could sell products all over the world (global)
– Transaction costs reduced (cost of participating in the market) Cost of participating in the market: it becomes easier to participate in the market
• Global reach
– Transactions cross cultural and national boundaries • Universal standards
– One set of technology standards: Internet standards Makes it easier for businesses to communicate in a standardized way
• Richness
– Supports video, audio, and text messages
Richness of information is much bigger than if you, for example, buy a book or a brochure • Interactivity
• Information density
– Greater price and cost transparency More information available
• Personalization/customization
For example: kinepolis.be: they use cookies and based on these cookies websites will be diferent for you than for (for example) your girlfriend
• Social technology
– Promotes user content generation and social networking Creating content yourself on the internet: for example: Pinterest
Features are quite unique as compared to the physical market place: difficult to reach in the physical market place
14. Which systems do we use by semi-structured and structured decisions?
Unstructured data (passive knowledge, knowledge in a video, e-mail) vs structured data (book, PowerPoint)
Enterprise-wide knowledge management: store, process and disseminate all types of knowledge in the organization (when most of the knowledge is unstructured or semi-structured)
• Three major types of knowledge in an enterprise – Structured documents
Reports, presentations Formal rules
– Semi structured documents E-mails, videos
– Unstructured, tacit knowledge
• 80% of an organization’s business content is semi structured or unstructured 15. predictive analytics?
Predictive Analytics
We are going to predict, for example: who is coming to buy our product? Use BI tools to get better inside information and to try to segment your 1000 customers into those who are likely to buy your product and those who are not going to buy your product
Focus your marketing and sales campaign on the people who are likely to buy your product: cost efficient
• Uses variety of data, techniques to predict future trends and behavior patterns – Statistical analysis
– Data mining – Historical data – Assumptions
• Incorporated into numerous BI applications for sales, marketing, finance, fraud detection, health care
– Credit scoring
– Predicting responses to direct marketing campaigns
Fraud detection: to see how flow of financial information goes to the markets and based on the flows to see in which organizations there can be fraud
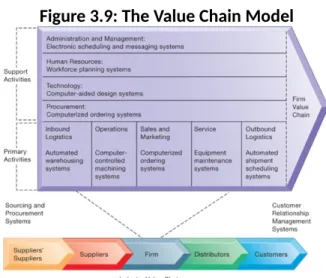
16. Explain value chain, draw, link with IT and more specific with ERP, CRM SCM The Business Value Chain Model
Tries to explain how a company creates value for the customer; always have primary and secondary activities
– Firm as series of activities that add value to products or services – Highlights activities where competitive strategies can best be applied
• Primary activities vs. support activities
– At each stage, determine how information systems can improve operational efficiency and improve customer and supplier intimacy
– Utilize benchmarking, industry best practices
Figure 3.9: The Value Chain Model
Primary activities can only operate if there are supporting of secondary activities Connection to IT? IT can help us make a specific activity more efective and efficient Link wit ERP: Synergies
Whole value chain has become digitalised: organizations use software to make those activities more efective and efficient in ERP system
IT helps us to create synergies
• When output of some units are used as inputs to others, or organizations pool markets and expertise
Link wit CRM
CRM systems provide information to coordinate all of the business processes that deal with customers, sales, marketing and service to optimize revenue and customer satisfaction. These are parts of the value chain
Link with CSM
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Systems
Information system that will help u optimise your supplies: system will automatically see what is still in stock and see if your close to having nothing (in a shop for example)
• Manage firm’s relationships with suppliers • Share information about:
– Orders, production, inventory levels, delivery of products and services • Goal:
– Right amount of products to destination with least amount of time and lowest cost
optimize the value chain 17. B2B/C2C/exchange?
Types of E-commerce: In the end these businesses have to make money • Three major types
– Business-to-consumer (B2C) Example: Zalando – Business-to-business (B2B)
Example: adobe, American express – Consumer-to-consumer (C2C)
Example: E-bay 18. Highest level of information system ESS
19. Wat is geen concurrerende kracht? Technology
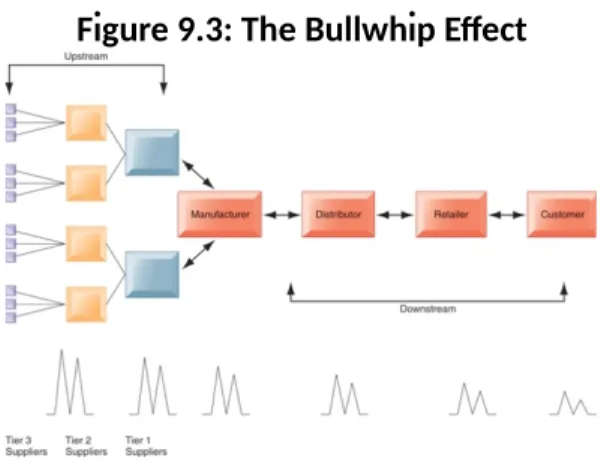
20. Supply chain + bullwhipefect Supply Chain Management
• Importance of timely and accurate information
Supply chain where all the elements in the supply chain will keep stock: costly business: we have to make our supply chain efficient: timely and accurate is important
– Inefficiencies cut into a company’s operating costs
Can waste up to 25 percent of operating expenses – Just-in-time strategy
Components arrive as they are needed
Finished goods shipped after leaving assembly line – Safety stock: Bufer for lack of flexibility in supply chain
If organizations are at huge uncertainty they will keep safety stock: very expensive – Bullwhip efect
Information about product demand gets distorted as it passes from one entity to next across supply chain
Happens in the supply chain when information is not communicated in the right phase in the supply chain the bullwhip efect
Figure 9.3: The Bullwhip Effect
Local retailer makes a short time promotion campaign for milk: as a result of the short time promotion campaign the demand will go up: if it’s not communicated in the supply chain that this was a one time, all the other players in the supply chain might increase their stock: they are preparing for the next time it happens: is a huge waste: it is not happening so we have to see that the information in the supply chain is timely and accurate: information systems will help to ensure better flows of information in the suplpy chain
21. Diference between niche firm and keystone firm? • Keystone firms (eg. Apple)
They provide a platform
• Niche firms (eg. developers of Apps)
Thousands of little companies that make apps for the iPhone
Individual firms can consider how IT will help them become profitable niche players in larger ecosystems
22. 2 disadvantages and 2 advantages of cloud computing, link with article IT doesn’t matter
– Cloud computing Disadvantage:
- Risk that data leaks on the internet
- Cloud applications reside in large remote data centers and server farms, to keep costs low, cloud computing providers often distribute work to data centers around the world so you my not know precisely where your data is being hosted
Advantage:
- Cost reduction - Standardization of IT Link:
Business technologies can really impact the businesses, cloud computing can impact the traditional companies.
23. WPA2 specification?
– Replaces WEP with stronger standards – Continually changing, longer encryption keys
24. Aisec case
Salesflare? Intelligent sales CRM allows you to focus on customers instead of data. Salesflare gathers contact and company information from e-mail signatures, social profiles and more save time entering data
save time reporting actions save time finding documents
You see all opportunities in one smart overview, automatic to do list: less work more sales 25. BPR, link with e-commerce
Business Process Redesign
• Business process management (BPM)
Always about the business process: how technology can innovate the business process?: how change a process by using technology ?
– Variety of tools, methodologies to analyze, design, optimize processes – Used by firms to manage business process redesign
• Steps in BPM
– Identify processes for change
One of the most important strategic decisions that a firm can make is nog deciding how to use computers to improve business process but understanding what business processes need improvement. Managers need to determine what business processes are the most important and how improving these processes will help business performance.
– Analyze existing processes (see 13.2)
Existing business processes should be modeled and documented, nothing inputs, outputs, resources, and the sequence of activities. The process design team identifies redundant steps, paper-intensive tasks, bottlenecks, and other inefficiencies.
– Design the new process (see 13.3)
Once the existing process is mapped and measured in terms of time and cost, the process design team will try to improve the process by designing a new one. A new streamlined ‘’to-be’’ process will be documented and modeled for comparison with the old model
– Implement the new process
Once the new process had been thoroughly modeled and analyzed, it must be translated into a new set of procedures and work rules. New information systems may have to be implemented to support the redesigning process. The new process and supporting systems are rolled out into the business organization. As the business starts using this process, problems are uncovered and addressed. May recommend improvements.
– Continuous measurement
Once a process has been implemented and optimized, it needs to be continuously
measured. Why? Process may deteriorate over time as employees fall back on old methods, or they may lose their efectiveness if the business experiences other changes.
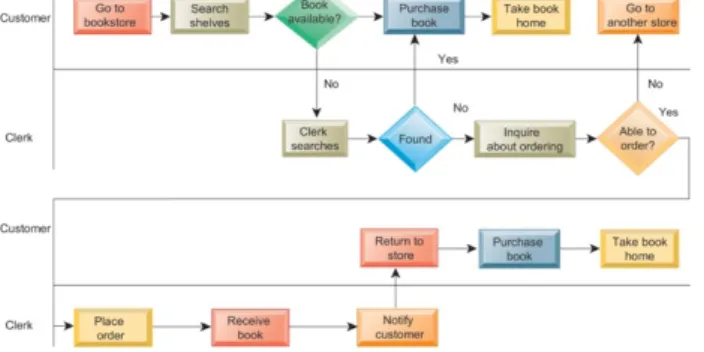
Figure 13.2: As-is Business Process for Purchasing a Book from a Physical Bookstore
View of a business process management tool
First step: understand the business process: business process management tool will help to visualized how a business process is organized/working
Whole flow of buying a book is decomposed into sub steps: how can I for example make a step more efficient?
Figure 13.3: Redesigned Process for Purchasing a Book Online
Business process was dramatically made more simple: bringing in technology which allows us to make the complex business process more efficient: when you can reduce the business process it will be cost efficient
Automate or redesign steps Link with e-business?
E-business helps with capturing the problems, improving and implementing: e-business refers to the use of digital technology and the internet to execute the major business processes in the enterprise.